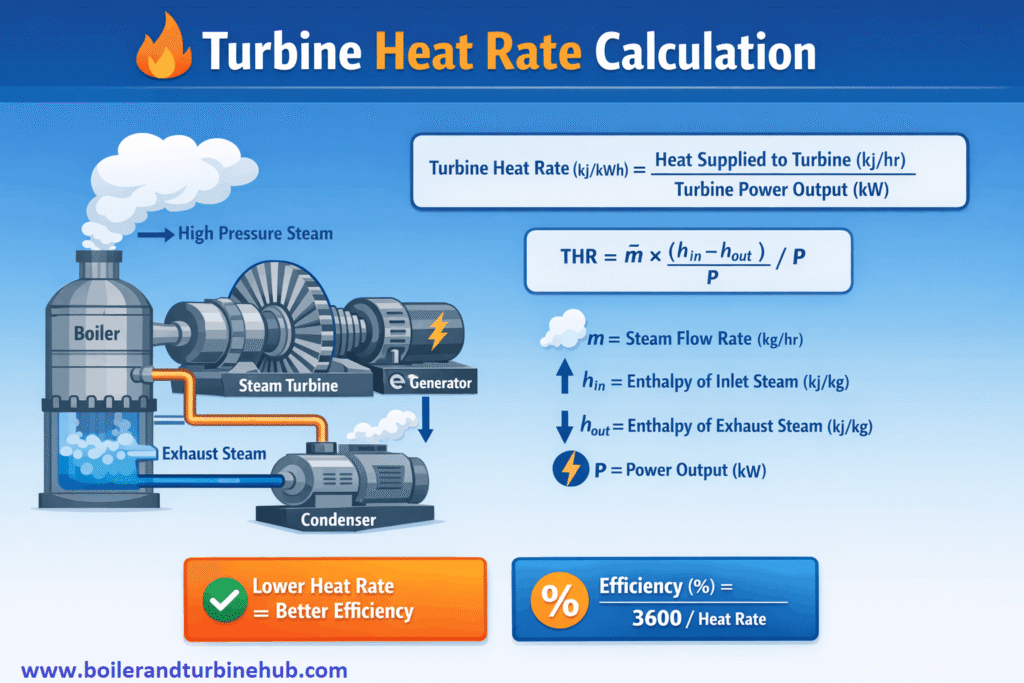
Turbine heat rate is the amount of heat input to the Turbine to generate unit power.
It is the ability of Turbine to generate power.
Lower the heat rate higher the Turbine efficiency and vice versa.
Turbine Heat Rate (kcal/kWh)=Turbine power output (kW) / Heat supplied to turbine (kcal/hr)
i.e
Turbine Heat Rate (kcal/kWh)=Steam flow X (Inlet steam enthalpy-Exhaust steam enthalpy) / Turbine power output (kW)
What is the relation between Turbine heat rate and efficiency?
Turbine efficiency = 860 X 100 / Turbine heat rate
What is the significance of Turbine Heat rate?
Turbine heat rate Indicates turbine performance
Used for performance testing & benchmarking
Helps identify efficiency deterioration
Affects overall plant heat rate and fuel consumption
What are the actors Affecting Turbine Heat Rate?
1. Main Steam Pressure and Temperature
Higher pressure and temperature increase the available energy in steam and improve turbine efficiency. Any deviation from design conditions increases heat rate.
2. Condenser Vacuum
Poor vacuum raises exhaust pressure, reducing turbine expansion ratio and increasing heat rate. Cooling water temperature, fouling, and air ingress strongly influence vacuum.
3. Steam Flow and Load
Turbines operate most efficiently near rated load. Part-load operation usually increases heat rate due to throttling and control losses.
4. Steam Quality
Moisture content in steam causes blade erosion and efficiency loss, increasing heat rate.
5. Turbine Blade Condition
Deposits, erosion, corrosion, or damage to blades reduce aerodynamic efficiency.
6. Seal Leakage
Worn labyrinth seals allow steam leakage, directly increasing heat rate.
7. Gland Sealing System Performance
Ineffective sealing allows air ingress and steam loss.
8. Control Valve Condition
Erosion or partial blockage increases throttling losses.
9. Bearing and Mechanical Losses
Poor lubrication or misalignment increases mechanical losses.
What is the difference between Turbine Heat Rate and Plant Heat Rate?
- Turbine Heat Rate considers only turbine performance.
- Plant Heat Rate includes boiler efficiency, turbine efficiency, generator efficiency, and auxiliary power consumption.
Plant heat rate is always higher than turbine heat rate because it accounts for additional losses in the entire power generation cycle.
What are the major reasons for reduction of Turbine heat rate?
Lower main steam pressure and temperature
- Lower vacuum
- Lower power output
- Fouled condenser tubes
- Air leakage into condenser
- Worn seals and blades
- Poor steam quality
- Degraded control valves
- Operation away from design load
- Improper maintenance practices
How do you improve Turbine heat rate?
- Maintaining designed input and out put steam parameters
- Optimising bleed steam flow
- Maintaining higher vacuum
- Keeping good maintenance practices
- Upgrade Components: High-efficiency blades and advanced sealing technologies reduce losses.
- Monitor Performance Trends Track heat rate regularly and compare with baseline data.
- Skilled operation.
Calculation of Heat rate:
Turbine heat rate calculation depends on the type of power plant and its operation condition.
For example:
Thermal power plant Turbines heat rate can be calculated as;
Turbine heat rate of a thermal power plant during normal O&M condition
Turbine Heat Rate (THR) = (Steam flow X Enthalpy of steam-Feed water flow X Enthalpy of feed water)/Power generation
A 10 MW Turbine has inlet steam flow 50 TPH at pressure & temperature 67 kg/cm2 & 490 Deg C respectively, then calculate the Turbine heat rate & Turbine efficiency. Consider feed water temperature at economiser inlet is 130 deg c & flow is 51 TPH.
We have;
Turbine power generation capacity = 10 MW
Steam flow = 50 TPH
Main steam enthalpy at above parameters = 811 kcal/kg
Feed water flow = 51 TPH
Feed water enthalpy at 130 deg C Temperature = 131 kcal/kg
Turbine Heat Rate (THR) = (Steam flow X Enthalpy of steam-Feed water flow X Enthalpy of feed water)/Power generation
Turbine Heat Rate (THR) = (50 X 811-51 X 131) / 10 = 3386.9 kcal/kg
Cogeneration Turbine heat rate
In case of Co-gen, Turbine heat rate is calculated by considering extractions and return condensate received.
Type-1
Co-gen-THR =((Turbine inlet steam flow X its Enthalpy)-(Process steam flow X Enthalpy Exhaust steam flow X Enthalpy)) / Power generation
Type-2
Co-gen-THR =((Turbine inlet steam flow X its Enthalpy + Process return condensate flow X its Enthalpy + Make up water flow X Its enthalpy)-(Process steam flow X Enthalpy + Feed water flow X Enthalpy)) / Power generation
A 10 MW condensing cum extraction turbine has inlet steam flow 50 TPH at 67 kg/cm2g pressure and 490 0C temperature, it has one bleed at 10 kg/cm2g pressure and temperature 190 0C at flow 7 TPH and extraction at 2.5 kg/cm2g pressure and temperature 150 0C at flow 30 TPH. Remaining steam goes to condenser at exhaust pressure 0.09 kg/cm2a.Calculate the turbine heat rate and thermal efficiency by using both formulae.
Consider steam given to process is = 7 TPH from bleed & 28 TPH from extraction and return condensate being 90% at temperature 80 & 105 deg C respectively.
Feed water inlet temperature at economiser is 130 deg C
DM water make up is 11% at temperature 28 deg C
Given that,
Power generating capacity of turbine = 10 MWH
Q1 = 50 TPH
Enthalpy h1 at 67 kg/cm2g and 490 C = 811 kcal/kg
Q2 = 7 TPH
h2 at 10 kg/cm2g and 190 C = 664 kcal/kg
Q3 = 30 TPH
h3 at 2.5 kg/cm2g and 150 C = 658 kcal/kg
Condenser steam flow Q4 = Q1-Q2-Q3 = 50-7-30 = 13 TPH
Enthalpy h4 at exhaust pressure = 44.06 kcal/kg
Formula-1
Cogen-Turbine heat rate (THR) = (Input heat to turbine- Sum of extraction and exhaust heat)/Power generation
= ((Q1 X h1)-(Q2 X h2+Q3 X h3 +Q4 X h4))/Power generation
= ((50 X 811)-(7 X 664 +30 X 658 + 17 X 44.06))/10
= 1841.3 kcal/kwh
Formula-2
Co-gen-THR =((Turbine inlet steam flow X its Enthalpy + Process return condensate flow X its Enthalpy + Make up water flow X Its enthalpy)-(Process steam flow X Enthalpy + Feed water flow X Enthalpy))Power generation
THR =((50 X 811 +(7 X 90% X 81+ 28 X 90% X 107) +50 X 11% x 29)-(7 X 664 +28 X 658 + 51 X 132))/10
THR =1412 kcal/kwh
Turbine thermal efficiency = (860 X 100)/Turbine heat rate
= (860 x100)/1412
= 60.9%