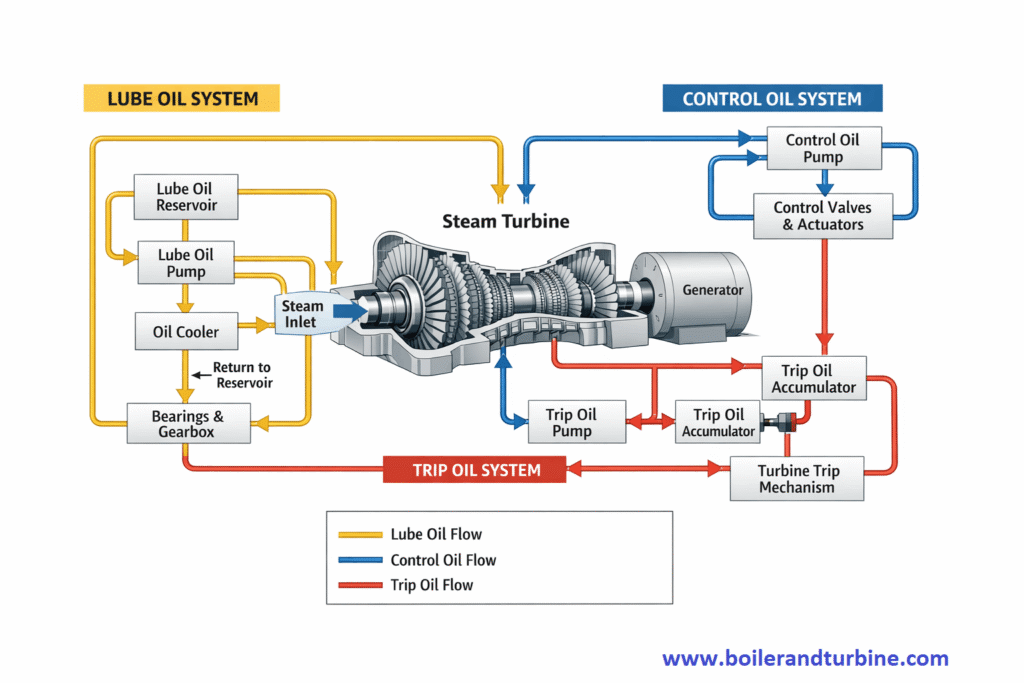
Steam turbines rely on multiple oil systems to ensure smooth operation, safe shutdown, and long equipment life. Among these, Control Oil, Trip Oil, and Lubricating Oil (Lube Oil) play distinct but interrelated roles.
How does Lube oil system work?
Lube oil is also called as Lubricating oil, Lube oil forms a protective oil film between moving parts to reduce friction and wear.
Lube oil lubricates following moving parts;
Turbine all bearings
Gear box bearings
Alternator bearings
What is the function of Lube oil in Turbines?
Lube oil Reduces friction between journal bearings and shaft bearing and also helps in cooling and flushing the contaminants from bearing
It also performs;
- Prevents corrosion and oxidation
- Supplies oil for jacking system and turning gear
- Carries away heat generated in bearings
What are the typical characteristics of Lube oil in turbine?
- High viscosity as compared to trip oil and control oil
- Low operating pressure ( 1 to 2.5 Kg/cm2) as compared to trip oil and control oil
- Operating oil pressure 40 deg C to 60 deg C
- High flow rate compared to control oil
- Filtration is coarse as compared to control oil ( 25 microns to 40 microns)
Control Oil
Control oil acts as a hydraulic medium to position and modulate steam control valves according to load demand.
Control oil is a high-quality hydraulic oil supplied at relatively higher pressure than lube oil. It operates the governor system, servo valves, and hydraulic actuators.
What are the main functions of control oil?
- Converts control signals into mechanical movement
- Precisely opens or closes steam valves
- Maintains turbine speed and load
What are the typical characteristics of Control oil in turbine?
- Low viscosity as compared to Lubel oil
- Higher operating pressure ( 6 to 25 Kg/cm2) as compared to trip oil and control oil
- Operating oil pressure 50 deg C to 60 deg C
- Lower flow rate compared to control oil
- Filtration is fine as compared to control oil ( 10 microns to 25 microns)
- Fast response time
What are the typical components of control oil system?
Components of control oil system;
- Control oil pump
- Accumulator
- Fine filters (high micron rating)
- Servo valves
- Hydraulic actuators / servomotors
- Pressure regulating valves
In many modern turbines, control oil is derived from the same lube oil system and boosted to higher pressure by a control oil pump.
Trip Oil
Trip oil provides a fail-safe protection function. It ensures immediate closure of all steam admission valves during abnormal or emergency conditions.
Trip oil is a dedicated hydraulic oil circuit that keeps the turbine steam valves in the open position during normal operation. When a trip condition occurs, trip oil pressure is dumped instantly, causing all main steam and governing valves to snap shut.
In many designs, trip oil is taken from the control oil or lube oil system and routed through trip devices.
What are the main functions of Trip oil?
- Keeps trip pistons pressurized during normal operation
- On pressure loss, springs close all stop and control valves instantly
- Acts on signals from mechanical, hydraulic, and electronic protections
What are the key components of trip oil system?
- Trip oil header
- Mechanical overspeed trip device
- Solenoid trip valves
- Emergency stop valve trip relays
- Trip oil dump valves
- Accumulators (in some systems)
What are the typical characteristics of Trip oil in turbine?
- Low viscosity as compared to Lube oil
- Higher operating pressure ( 6 to 25 Kg/cm2) as compared to Lube oil
- Operating oil pressure 50 deg C to 60 deg C
- Lower flow rate compared to control oil and Lube oil
- Filtration is fine as compared to control oil ( 10 microns to 25 microns)
- Fast response time
How does trip oil work?
After sensing any abnormal parameter, Trip signal actuates trip valve, Trip oil pressure collapses, Spring-loaded steam valves close rapidly and finally Turbine is isolated from steam.
| Sl No. | Lube oil | Control oil | Trip oil |
| 1 | Acts as bearing lubricator | Acts as hydraulic oil or control oil | Acts as trip oil |
| 2 | Does not initiates tripping of the Turbine | Does not initiates tripping of the Turbine | Initiates tripping of the Turbine |
| 3 | High operating viscosity | Low operating viscosity | Low operating viscosity |
| 4 | Higher operating flow | Lower operating flow | Lower operating flow |
| 5 | Low operating pressure | High operating pressure | Medium operating pressure |
| 6 | Filtration is not that much fine compared to Control oil and Trip oil | Filtration is fine | Filtration is fine |
| 7 | Performs cooling and flushing | Performs controlling action | Performs emergency trip action |
| 8 | Separate pump is available for Lube oil pumping | Separate pump is available or some times a tapping from lube oil is taken for controlling | Separate pump is available or sometimes a tapping from lube oil is taken for controlling |